
SolidWorks CAD software offers an intuitive interface, powerful modeling, and virtual prototyping capabilities. It streamlines design, enhances collaboration, and supports manufacturing, making it a top choice for engineering and product development.
Table of Contents
Selecting the appropriate CAD software is a critical decision that affects design efficiency, collaboration capabilities, and your organization’s bottom line. When comparing SolidWorks vs other CAD tools, design professionals consistently find that SolidWorks offers exceptional value across multiple areas.
SolidWorks offers a comprehensive ecosystem that supports the entire product development lifecycle – from initial concept sketches through detailed 3D modeling to manufacturing documentation and analysis. As a leading 3D CAD modeling software, its intuitive interface, powerful modeling capabilities, and extensive feature set make it exceptionally versatile across industries, including automotive, aerospace, consumer products, and industrial equipment manufacturing.
Globally, manufacturers of consumer products, industrial equipment, automotive parts and construction equipment rely on SolidWorks CAD software modeling and virtual prototyping capabilities.
While there are other alternatives in the market, SolidWorks continues to distinguish itself through its balance of accessibility and advanced functionality. Understanding these advantages is essential for organizations seeking to optimize their design processes and maintain competitive advantage in increasingly complex markets.
Understanding how SolidWorks measures against its primary competitors provides a critical context for making informed software decisions. The following comparison highlights the distinctive strengths and capabilities of major CAD platforms across several essential criteria:
| Feature | SolidWorks | Inventor | AutoCAD | Creo | Solid Edge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Curve | Shorter learning curve with intuitive interface | Moderate learning curve; benefits Autodesk users | Steeper learning curve for 3D work; familiar for 2D users | Steepest learning curve with powerful but complex interface | Moderate learning curve with synchronous technology |
| Modeling Capabilities | Both parametric and direct modeling with superior surfacing tools | Strong parametric modeling with limited direct editing | Limited 3D modeling capabilities compared to dedicated 3D tools | Advanced parametric capabilities with reasonable direct editing | Synchronous technology balances parametric and direct approaches |
| Large Assembly Handling | Excellent performance with specialized large assembly tools | Good performance with some limitations | Limited large assembly capabilities | Superior performance for complex assemblies | Good performance with mid-range assembly complexity |
| Industry Adoption | Widespread across manufacturing, consumer products, medical devices, industrial equipment | Strong in manufacturing and mechanical design | Dominant in architecture, construction, and 2D drafting | Preferred in aerospace, automotive, and high-complexity industries | Popular in machinery, sheet metal, and process industries |
| File Compatibility | Supports most major file formats with excellent translation | Good compatibility within Autodesk ecosystem | Excellent 2D compatibility, limited 3D translation | Moderate compatibility with focus on precision | Good compatibility with some translation limitations |
| Design Automation | Advanced automation through DriveWorks integration | Decent automation capabilities through iLogic | Limited automation capabilities | Strong automation through Pro/PROGRAM | Moderate automation capabilities |
| Market Position | Holds a major portion of professional CAD market share | Second-tier market position with strong Autodesk ecosystem integration | Primarily 2D-focused with 3D capabilities; the largest installed base for 2D work | Established enterprise solution with complex capabilities | Mid-market solution with growing user base |
SolidWorks continues to stand out among CAD platforms by delivering substantive advantages throughout the product development lifecycle. These capabilities directly translate into improved productivity, reduced costs, and accelerated time-to-market.
Here are some major benefits of SolidWorks for manufacturing as well as product design:
Discover how SolidWorks can transform your product development cycle.
Learn more today »SolidWorks continuously evolves with enhanced modeling tools, smart automation, and improved collaboration features to streamline engineering workflows.
SolidWorks stands apart from the variety of CAD tools available today as a leading CAD software that helps end customers streamline product development processes efficiently, addressing not only their present requirements but also preparing them for future needs.
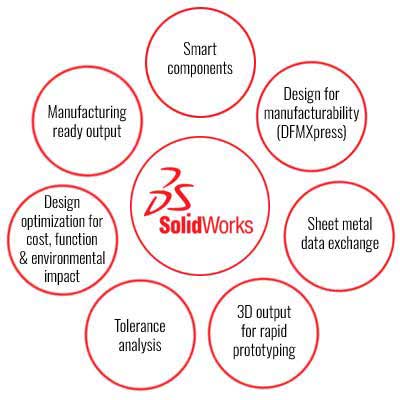
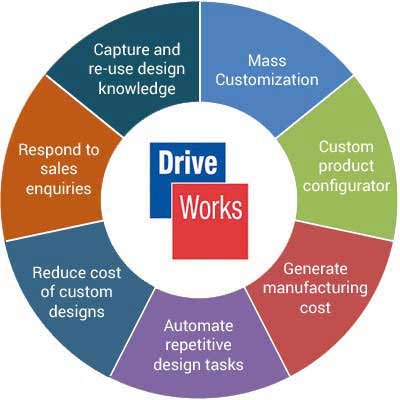
SolidWorks delivers exceptional value through an integrated set of powerful features designed to address complex engineering and manufacturing challenges. Key capabilities include:
These advanced capabilities enable diverse SolidWorks industry applications, from aerospace and automotive design to consumer electronics and medical device development. Organizations across manufacturing sectors leverage these specialized tools to address industry-specific challenges while maintaining design consistency.
With over 3.1 million SolidWorks users globally across diverse industries, finding truly qualified design expertise can be challenging. Partnering with certified SolidWorks professionals provides significant advantages for product development initiatives. SolidWorks certification validates a designer’s proficiency, ranging from basic modeling skills (CSWA) to comprehensive mastery (CSWE).
The certification level directly affects design efficiency and output quality. While Associates (CSWAs) competently handle fundamental modeling tasks, Professionals (CSWPs) demonstrate advanced skills in complex geometry creation and assembly management, resulting in faster design cycles. Experts (CSWEs) provide the highest efficiency through workflow optimization and error reduction, particularly valuable for sophisticated projects requiring exceptional precision.
Specialty certifications in sheet metal, weldments, surfacing, and mold making further enhance efficiency for specialized manufacturing requirements. These certified professionals apply industry best practices and specialized tools that reduce design time and material waste in their respective domains.
Working with appropriately certified SolidWorks professionals ensures your critical designs receive competent handling from specialists who thoroughly understand relevant software features. Their proven modeling and evaluation expertise allows them to address design challenges quickly and effectively, helping you reduce development time and costs while improving final product quality.
As engineering challenges grow increasingly complex, selecting the right CAD platform becomes a strategic decision with far-reaching implications. SolidWorks continues to serve as an industry-leading solution that balances powerful capabilities with accessibility, positioning it among the best CAD software for engineers seeking both performance and usability.
Organizations embracing SolidWorks position themselves to meet both current market demands and future design requirements through enhanced efficiency, improved collaboration, and streamlined manufacturing processes. Using SolidWorks with expert training leads to a powerful design system that helps companies be more creative and competitive.
Unlock manufacturing efficiency through advanced SolidWorks features.
Contact us »You may also like
From 2D to 3D: Why Architects are Switching to BIM Modeling
10 Essential Best Practices for BIM in MEP Engineering
How 3D Scan to Revit Can Solve As-Built Modeling Challenges
DXF Files in SolidWorks: How to Import and Export Them